Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis typically involves the use of specific ointments to relieve symptoms and control inflammation. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that primarily occurs in areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It is characterized by erythema, oily scaling, and mild itching.
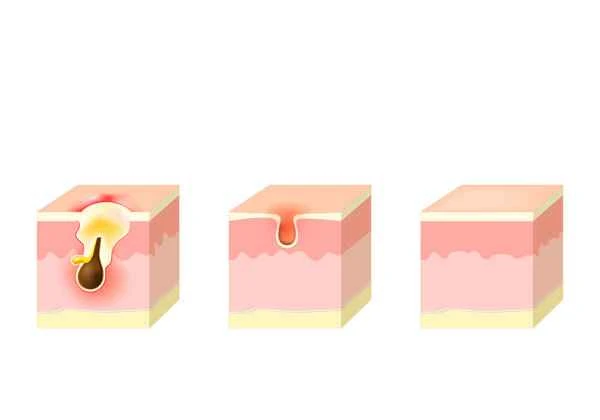
Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis typically includes antifungal creams and corticosteroid creams. Antifungal creams, such as ketoconazole, inhibit the growth of Malassezia, the fungus that causes seborrheic dermatitis, thereby reducing inflammation and symptoms. Corticosteroid creams can relieve inflammation and itching, but long-term use may lead to side effects such as thinning of the skin. Doctors will choose the appropriate cream based on the patient's specific condition. Maintaining good personal hygiene while using creams is also very important, such as regularly cleansing the skin and avoiding the use of overly oily skincare products.
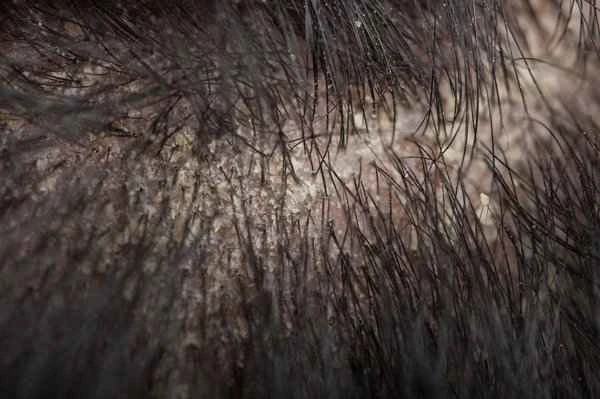
Choosing the right ointment is crucial when treating seborrheic dermatitis, but it's also important to be aware of potential risks and common misconceptions. Treating seborrheic dermatitis is a long-term process requiring patience and consistent treatment. While corticosteroid ointments can provide quick symptom relief, long-term use may lead to side effects such as thinning of the skin and pigmentation. Therefore, it's essential to use them appropriately under the guidance of a doctor. Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis involves more than just topical medications; it also requires lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining good personal hygiene and avoiding excessive cleansing and skin irritation.
[Management Tips]
1. Use the ointment recommended by your doctor regularly and follow your doctor's instructions for treatment.
2. Maintain good personal hygiene habits and avoid using overly oily skin care products.
3. If symptoms worsen or persist without relief, seek medical attention promptly.


