Scar tissue inflammation refers to an inflammatory reaction in scar tissue, requiring comprehensive treatment to relieve symptoms and promote recovery.
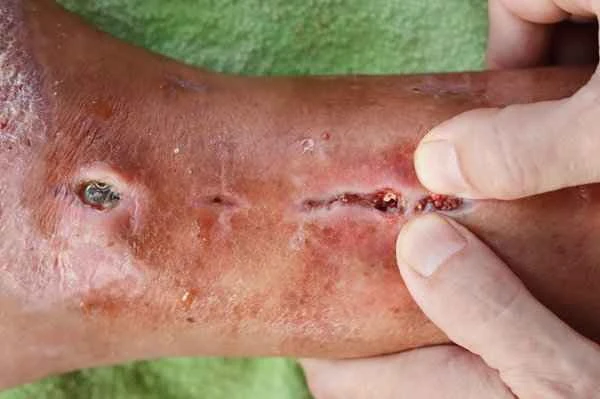
Treatment of keloid scarring requires a comprehensive consideration of the cause and severity of the inflammation, as well as the patient's overall health. Treating the underlying cause of the inflammation is crucial, and this may include surgical removal of scar tissue, medication to control the inflammatory response, and measures to prevent infection. Regarding medication, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and pain, but should be used under the guidance of a physician to avoid potential side effects. Topical antibiotics or antifungal medications can prevent or treat secondary infections. Keeping the wound clean and dry is equally important during treatment to promote healing. For severe or persistent keloid scarring, further surgical intervention, such as scar excision or skin grafting, may be necessary to improve symptoms and restore function.
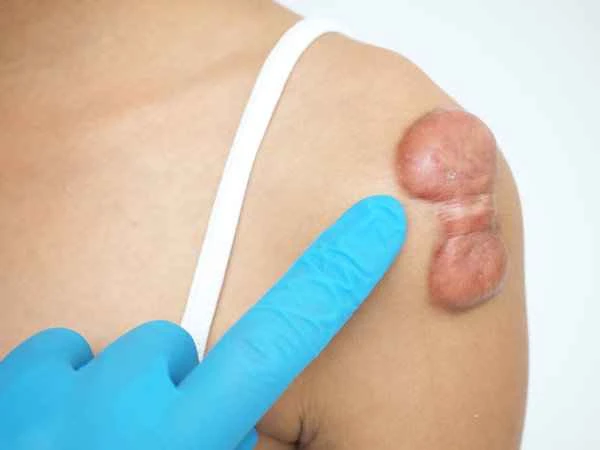
Patients may encounter some misconceptions when treating keloid scarring, such as believing that all cases can be resolved with simple medication or neglecting the importance of wound care. In reality, the treatment of keloid scarring requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including the cause and severity of the inflammation, as well as the patient's overall health. During treatment, patients should follow their doctor's advice and undergo regular follow-up examinations and evaluations to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the treatment plan.
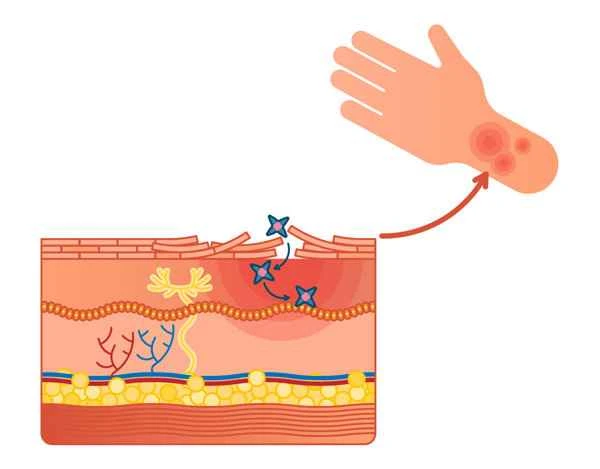

[Management Tip:]
1. Regular follow-up examinations to monitor inflammatory responses.
2. Keep the wound clean to prevent infection.
3. Use medication as prescribed to control inflammation.
4. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly.


