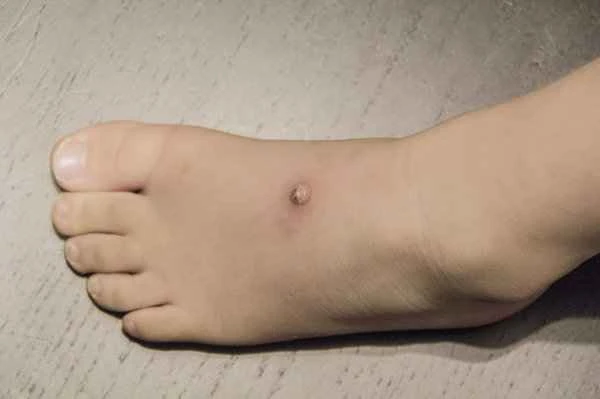
Blood tests for purpura involve assessing the type and severity of purpura through blood examinations. This test is crucial for diagnosing and treating purpura because it helps doctors understand the patient's blood condition and thus develop an appropriate treatment plan.

The importance of blood tests for purpura lies in their ability to provide crucial information such as platelet count, coagulation function, and the presence of abnormal antibodies in the patient's blood. This information is essential for determining the cause, type, and potential complications of purpura. Through these tests, doctors can more accurately assess the condition and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
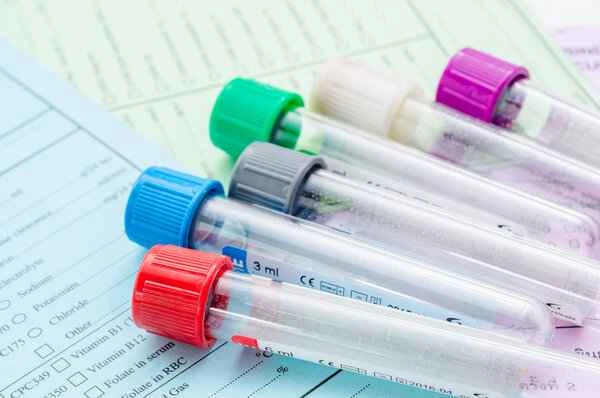
In practice, blood tests for purpura typically include a complete blood count, coagulation function tests, and platelet function analysis. These tests can reveal whether the platelet count is normal, whether there is a coagulation disorder, and whether there is an autoimmune reaction causing purpura. Through these detailed test results, doctors can better understand the patient's condition and develop a personalized treatment plan accordingly.
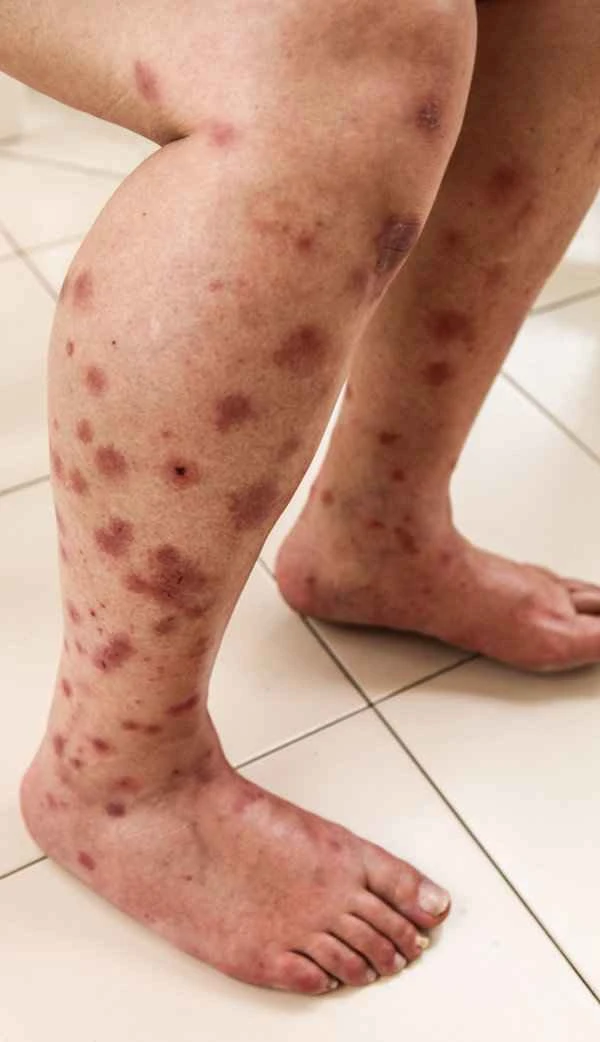
When interpreting test results, it's important to recognize that these values are only one part of assessing the condition. For example, a low platelet count may indicate thrombocytopenia, but this alone is not sufficient to diagnose purpura. Interpreting test results requires considering the patient's clinical symptoms and other test findings. Furthermore, patients should avoid self-interpreting test results and instead communicate fully with their doctor to understand the meaning of the results and follow the doctor's treatment recommendations.
【Useful Tips:】
1. Before undergoing blood tests for purpura, it is best to consult a doctor to understand the specific tests required.
2. Examination results need to be analyzed in conjunction with clinical symptoms and other examination results, and judgments should not be made based on a single indicator.
3. When interpreting inspection results, one should maintain an objective attitude and avoid over-interpreting or misunderstanding the results.
4. Follow your doctor's advice for treatment and have regular check-ups to monitor changes in your condition.