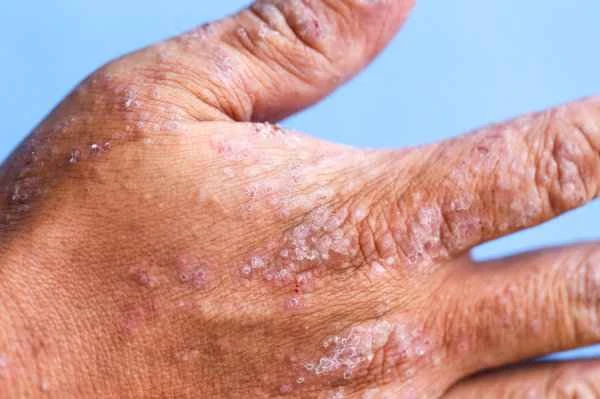
Patients with urticaria can take baths, provided it doesn't worsen their symptoms. Bathing itself doesn't directly cause or aggravate urticaria, but the method of bathing and environmental factors can influence the severity of symptoms. The water temperature should not be too hot or too cold, as extreme temperature changes can irritate the skin and exacerbate urticaria symptoms. Cleansing products used should be mild and non-irritating; avoid using shower gels or soaps containing strong chemicals, as these ingredients may trigger allergic reactions and worsen urticaria symptoms. Finally, post-bathing skin care is equally important; using gentle moisturizing products can help relieve dry skin and reduce the chance of urticaria flare-ups.
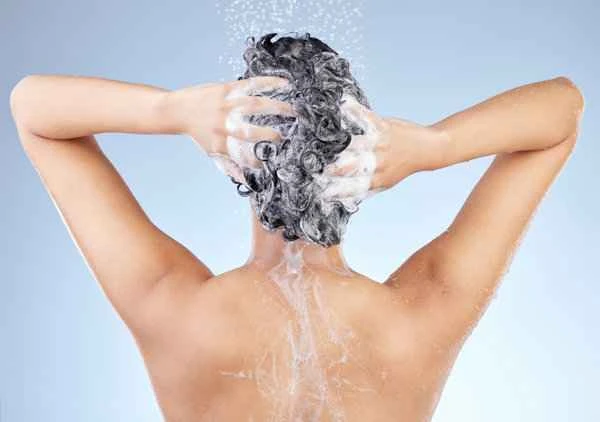

When treating urticaria (hives), it's important to avoid some common misconceptions. While bathing itself doesn't directly worsen urticaria, using harsh cleaning products or bathing in excessively hot or cold water can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Over-washing or prolonged soaking can also damage the skin's natural protective layer, making it more susceptible to external factors and increasing the risk of urticaria flare-ups. In managing urticaria, in addition to bathing methods and environmental factors, it's necessary to consider other factors that may influence symptoms, such as diet and environmental factors, for more comprehensive disease management.

[Management Tip:]
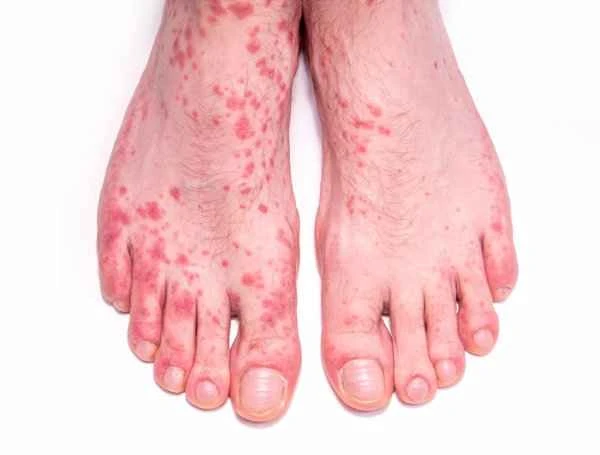
1. Choose mild and non-irritating cleaning products.
2. Avoid using water that is too hot or too cold when taking a bath.
3. Use moisturizing products to care for your skin promptly after showering.