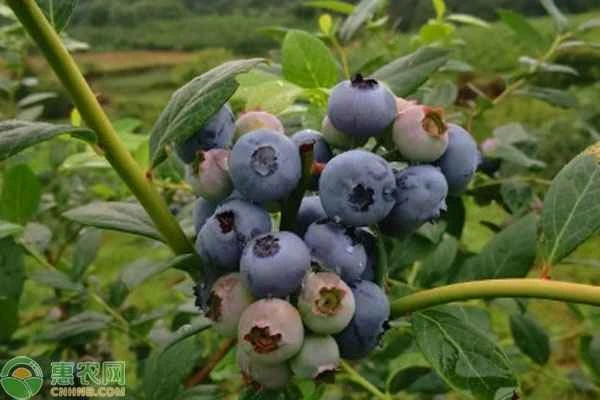
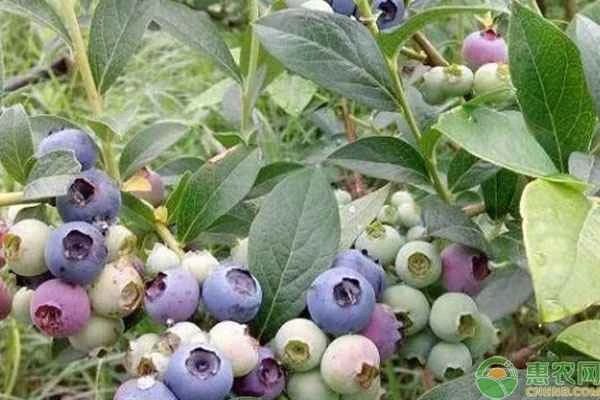
Blueberries are known as the "King of Berries ," prized not only for their delicious taste but also for their rich nutritional value. They are highly popular with consumers and have a promising future in cultivation. So how do you grow blueberries to ensure they thrive? Let's find out.
1. Soil preparation
Suitable soil standards for blueberry cultivation: pH value of 4.5-5.5 is optimal; organic matter content of 8%-12%; low salt content; electrical conductivity not exceeding 1000μS/cm, preferably below 200μS/cm; loose and well-drained soil, preferably sandy loam or sandy soil, not heavy or waterlogged, and with good irrigation conditions.

2. Selecting seedlings
Generally, 2-3 year old seedlings are selected, as these have a higher survival rate. The seedlings are typically over 30cm tall, but this varies depending on the variety. It's important to choose a variety suitable for the climate and soil conditions of your location.
3. Planting time
Spring or autumn are the best times to plant blueberries. Autumn planting can be done from September to November, while spring planting is best done from February to March.
4. Planting methods
Dig a hole slightly larger than the root system of the sapling at the selected location, with a depth approximately equal to the height of the root collar. Gently place the sapling into the hole, keeping it upright, then backfill with soil, compacting it to ensure there are no gaps around the roots. Water thoroughly after planting, ensuring the soil remains moist.

5. Key Management Points
(1) Watering: Blueberries are not tolerant of waterlogging, so water them appropriately to keep the soil moist but avoid water accumulation.
(2) Fertilization: In the early stage of planting, some organic fertilizers , such as compost or slow-release fertilizers , can be applied to promote the growth of blueberries.
(3) Pruning: Prune blueberry plants regularly to remove dead and diseased branches to promote the growth of new branches and the ripening of fruit.
6. Pest and disease control
Common diseases and pests affecting blueberries include powdery mildew, downy mildew, aphids, mites, and fruit flies. Prevention is key, along with integrated pest management. This includes protecting and utilizing natural enemies, maintaining ecological balance within the blueberry orchard, prioritizing physical and biological control methods, and using chemical control only when necessary.