The recurrence time after keloid removal on the earlobe varies from person to person. Some patients may experience a recurrence within a few months, while others may not experience a recurrence for many years. Keloid recurrence is related to a variety of factors, including individual constitution, postoperative care, and whether preventive measures were taken.
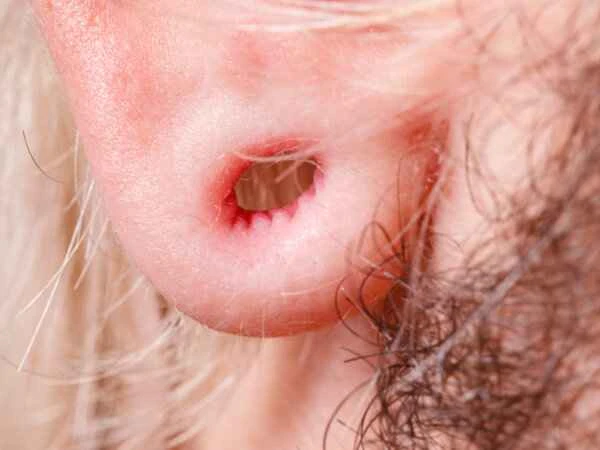
Keloids are overgrown scar tissues that typically form after skin trauma. Even after keloid removal, recurrence is possible without proper preventative measures. The timing of recurrence is influenced by various factors, including individual constitution, postoperative care, and the implementation of preventative measures. For example, some people are more prone to keloid formation, which may result in a shorter recurrence time after removal. Postoperative care also affects the likelihood of recurrence. Improper postoperative care, such as wound infection or excessive stretching, can also lead to keloid recurrence. To reduce the likelihood of recurrence, patients need to strictly follow their doctor's instructions after surgery, including keeping the wound clean and avoiding stretching or irritation.
[Prevention Tips:]
1. Regular follow-up examinations after surgery to monitor wound healing.
2. Avoid pulling or irritating the earlobe area.
3. Maintain good lifestyle habits and avoid bad habits such as smoking.
4. If redness, swelling, pain or other abnormal symptoms occur, seek medical attention promptly.


