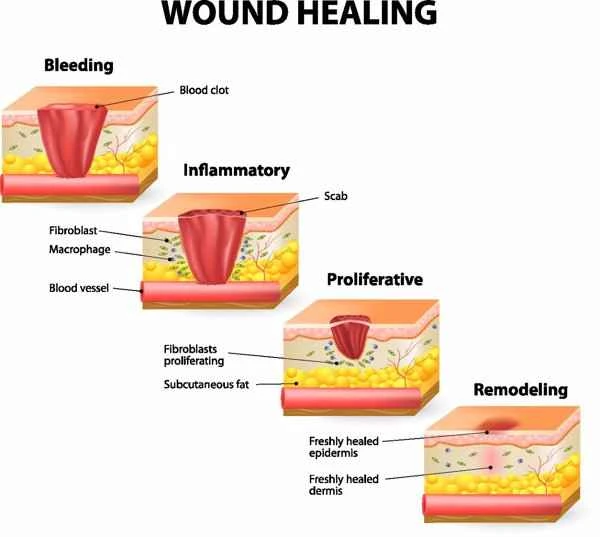
The management of scars primarily involves a range of methods to reduce their impact and promote healing. Scar formation is a natural response in the healing process after skin injury, but excessive scarring can lead to discomfort and even functional impairment. Treatment methods include medication, physical therapy, and surgical intervention, all of which work through different mechanisms to reduce scar formation or improve its appearance.
Drug therapy is a common approach to scar management, including the use of topical medications such as silicone sheets or gels. These medications keep the wound moist, promote skin healing, and reduce scar formation. Oral medications such as vitamin E and some anti-inflammatory drugs can also help reduce scarring. Physical therapy includes pressure therapy and laser therapy, which reduce scar hyperplasia by applying external pressure or utilizing the photothermal effect of lasers. Surgical intervention is suitable for severe scars, such as keloids or scar contractures, by surgically removing the scar tissue and then using skin grafts or other techniques to improve the appearance and function of the skin.
It's important to note that not all scars can be completely eliminated; some may require long-term management and maintenance. Side effects such as allergic reactions or infections may occur during scar treatment. Therefore, close monitoring of the patient's response and timely adjustments to the treatment plan are necessary. Furthermore, patients need to set realistic expectations for scar treatment to avoid psychological stress caused by excessive hopes.
[Management Tip:]
1. Use topical medications such as silicone sheets or gels to reduce scarring.
2. Perform regular skin care to keep the wound moist.
3. Seek medical attention promptly if infection or allergic reaction occurs.