White shrimp are delicious and nutritious, and can be used to cook a variety of dishes and make various flavorful snacks, making them very popular with consumers. Many farmers raise white shrimp , but their farming requires mastering certain techniques and management methods. Below, we will discuss the methods of raising white shrimp.
1. Pond conditions
Choose a pond with sufficient water, no pollution, and convenient drainage and irrigation for aquaculture. The bottom should have mud and sand, and the pond should be surrounded by a plastic film to prevent the invasion of natural enemies.
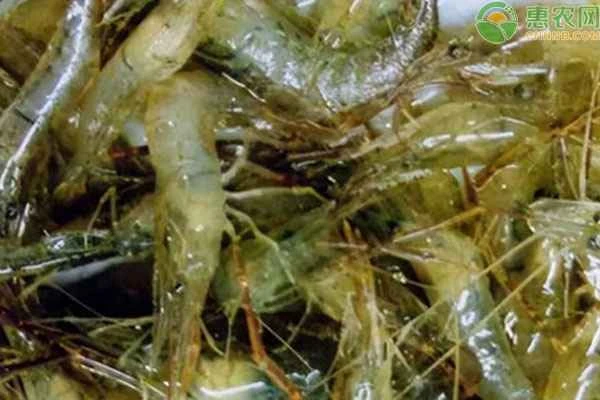

2. Shrimp larvae selection and transportation
Selecting high-quality shrimp larvae is key to successful shrimp farming. It is essential to choose larvae that are free from pathogenic bacteria and viruses and to ensure adequate oxygen during transportation.
3. Precautions for seedling release
Before stocking, the pond should be cleaned and disinfected to ensure that the water transparency is about 30 centimeters. At the same time, the stocking density should be controlled to 30,000 to 50,000 fish per acre.
4. Feeding
Feed them three times a day, using high-quality feed, and determine the amount to feed each time based on the growth and feeding habits of the white shrimp.
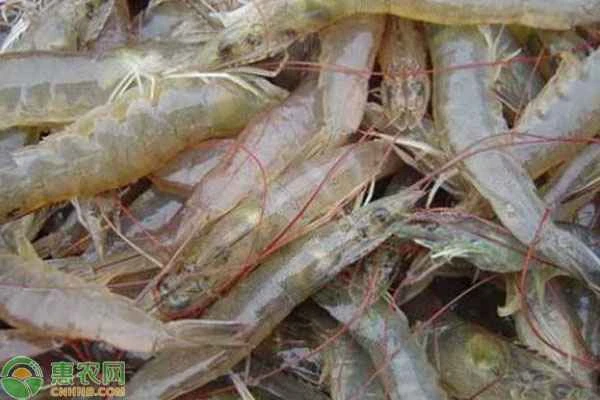

5. Water quality management
Water quality should be tested regularly, including indicators such as nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, and pH value, and water should be changed or added periodically to maintain appropriate transparency and water quality stability.
6. Disease prevention and control
Various diseases may occur during the farming of white shrimp. It is necessary to strengthen management and regularly use antibacterial and antiviral drugs for prevention and treatment.
7. Daily Management
Regularly observe the growth and activity of the white shrimp, promptly identify and address any problems, and ensure proper cleaning and maintenance of the pond.
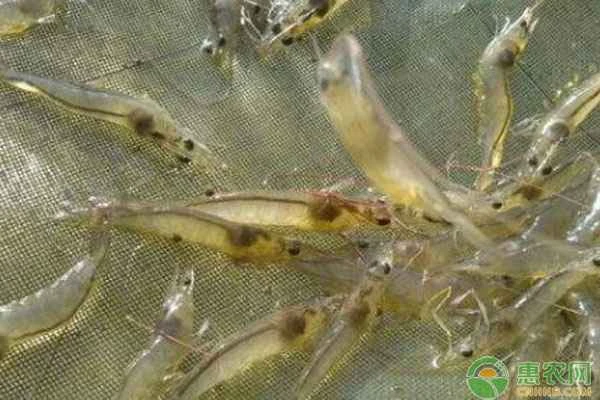

8. Timely fishing
Aquaculture farmers should develop reasonable fishing plans based on market demand and aquaculture conditions, fish in stages, maintain a supply of fish of all sizes, and avoid oversupply.