Celery is a very nutritious vegetable . Fresh celery leaves are bright green and have a crisp texture. Many celery growers encounter the problem of yellowing leaves. So, what causes celery leaves to turn yellow? Let's find out below.
1. Overwatering
Overwatering celery reduces the nutrient content around the roots, preventing them from breathing properly and causing root rot, resulting in yellowing and, in severe cases, wilting. It's important to drain excess water promptly and ensure proper ventilation and drainage in the field.
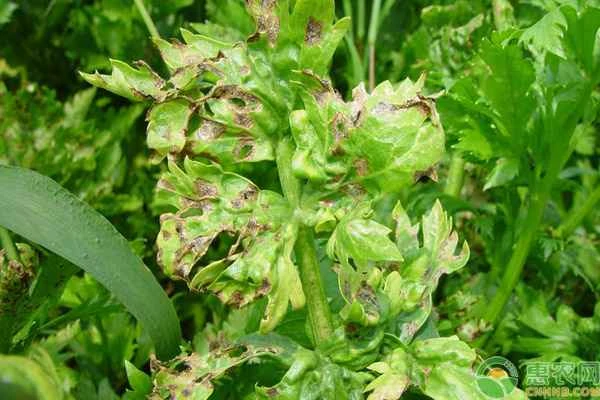

2. Insufficient watering
Insufficient watering of celery can lead to soil compaction, hindering normal root respiration and causing the leaves to turn yellow due to excessive water shortage. In this case, watering should be done.
3. Insufficient lighting
Insufficient sunlight or prolonged periods of cold, overcast weather during celery growth can cause yellowing leaves, leading to a decline in celery quality. Sufficient sunlight is essential to ensure celery leaves remain green and that the plant grows normally.
4. Temperature too high
Excessive temperature in celery greenhouses can also cause yellowing. If this occurs, shading and ventilation measures should be taken. The optimal temperature for celery growth is 15-20℃.

5. Lack of nitrogen fertilizer
Celery requires a significant amount of nitrogen for growth. A common cause of yellowing leaves is nitrogen deficiency. The yellowing starts in the older outer leaves, and as the deficiency worsens, even the younger leaves will turn yellow. The older outer leaves may also turn yellowish-white, eventually leading to the entire plant turning yellow. At this point, nitrogen fertilizer can be supplemented.
6. Potassium deficiency
Celery lacking potassium typically shows yellowing of the outer, older leaves first, accompanied by necrotic spots between the veins. In this case, potassium fertilizer should be applied.
7. Iron deficiency
When celery is deficient in iron, its leaves turn yellow and lose their green color. Foliar fertilization can be applied promptly; for iron deficiency, a 0.2% ferrous sulfate solution or a 0.2% ferric chloride solution can be sprayed.