Scar bleeding refers to bleeding in the scar tissue that forms after a surgical incision or other trauma has healed. Hemostasis with medication refers to controlling this bleeding through drug intervention.
Hemostasis for scar bleeding primarily relies on the application of topical hemostatic agents, which achieve their hemostatic effect through different mechanisms. Commonly used topical hemostatic agents include thrombin, gelatin sponge, and fibrin glue. Thrombin is an enzyme that directly promotes blood clotting; it accelerates platelet aggregation and fibrin formation, thus rapidly stopping bleeding. Gelatin sponge is a porous hemostatic material that absorbs blood and forms a gel-like structure, thereby aiding in blood clotting. Fibrin glue is a gel-like substance containing fibrin; it forms a physical barrier that helps blood clot and reduces bleeding.
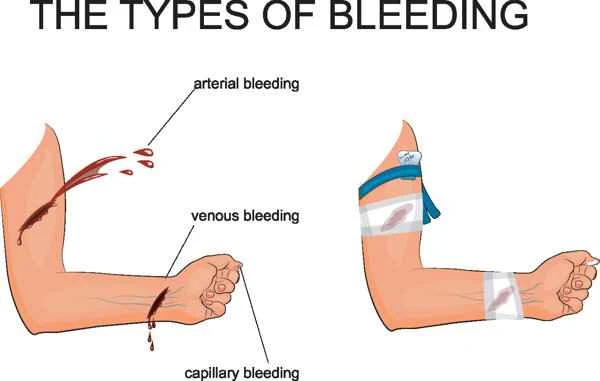
When using these medications, the appropriate medication should be selected based on the specific bleeding situation and the characteristics of the scar tissue, and it should be used correctly under the guidance of a doctor. During use, it is necessary to observe for any allergic reactions or other adverse reactions and report them to the doctor promptly.
[Management Tip:]
1. Before applying topical hemostatic agents, the wound should be cleaned to prevent infection.
2. After applying the medication, keep the wound dry and avoid getting it wet.
3. If persistent bleeding or other abnormalities occur, seek medical attention promptly.


