The process of removing residual skin scars essentially involves a series of treatments to promote the skin's self-repair and reduce the appearance of the scars. Scar removal involves multiple methods, including drug therapy, physical therapy, and surgical treatment, each with its specific mechanism of action and applicable situations.
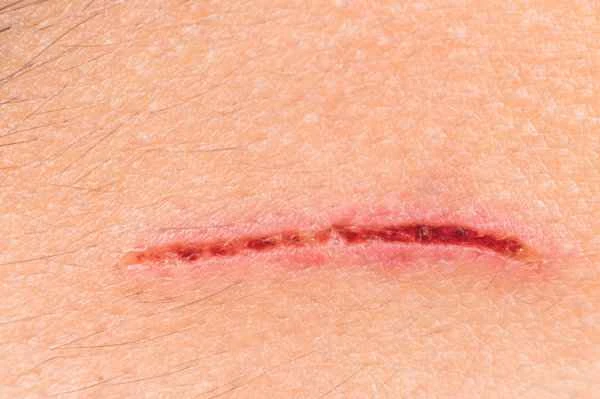
When treating residual skin scars, it's essential to first understand the type of scar, such as hypertrophic scars, keloids, or atrophic scars, as different types may require different treatment methods. Medication is a common method for scar removal, including the use of topical medications such as silicone gel sheets or gels. These medications help soften scar tissue, reduce redness and swelling, and flatten the scar. Oral medications such as vitamin E and vitamin C are also used to promote skin repair and reduce scar formation. Physical therapies such as laser therapy and microneedling stimulate the skin to produce new collagen, helping to improve the appearance of the scar. For more severe scars, surgical excision of the scar tissue followed by skin grafting or flap transfer may be necessary to achieve the best repair results.
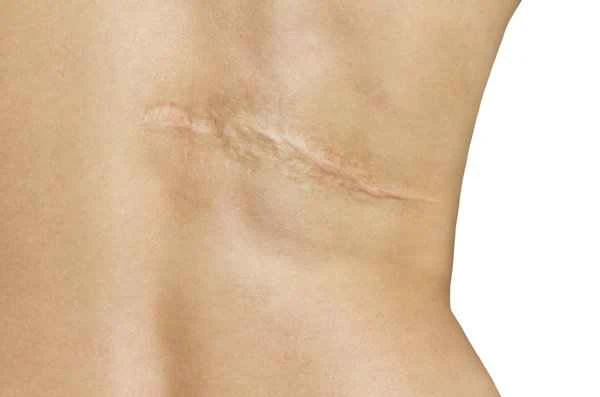
In treating residual skin scars, patients may encounter some misconceptions, such as believing that all scars can be completely removed, or incorrectly using treatments unsuitable for their scar type. In reality, scar removal is a gradual process; some scars may not disappear completely and can only be made less noticeable through treatment. When choosing a treatment method, the most suitable plan should be selected based on the specific type and extent of the scar, in conjunction with the professional advice of a doctor.
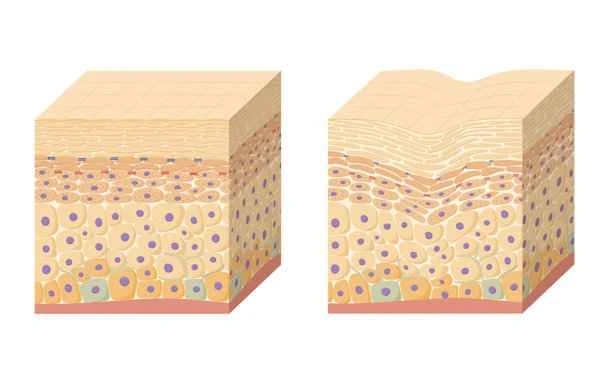
[Management Tip:]
1. Use topical medications recommended by your doctor regularly, such as silicone gel sheets or gels, to help soften scar tissue.
2. Avoid using medications or treatments that are not recommended by a doctor, as this may cause skin damage.
3. If symptoms such as changes in scar color, increased redness and swelling, or increased pain occur, seek medical attention promptly.


