Yellowing of the skin can be caused by a variety of reasons, a condition commonly known medically as jaundice. Jaundice is mainly characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, caused by elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow substance produced after the breakdown of red blood cells, and normally it is processed by the liver and excreted from the body.

Jaundice can be a sign of liver problems, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or bile duct obstruction. Hepatitis can be caused by viruses, such as hepatitis A, B, or C, or by alcohol, medications, or autoimmune disorders. If accompanied by symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, or dark urine, liver disease should be considered. Another possibility is related to problems with the biliary system, such as gallstones or bile duct stricture, which are usually accompanied by right upper quadrant pain or prolonged jaundice.
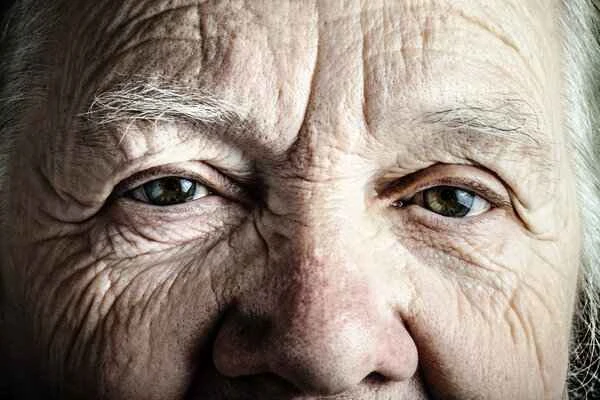

Elevated bilirubin levels may also be associated with hemolytic diseases, which cause red blood cells to rupture prematurely, thus increasing the concentration of bilirubin in the blood. If a patient also experiences symptoms such as itchy skin, dark urine, and light-colored stools, it may indicate hemolytic anemia or other blood disorders.
Jaundice is an important warning sign that the body may be experiencing a serious health problem. Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms appear, especially if jaundice is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, fever, extreme fatigue, or confusion. Jaundice is not always caused by liver disease, so do not try to guess the cause without a professional diagnosis. Finally, although jaundice may be related to diet or medication in some cases, these conditions usually do not cause persistent jaundice.
[Prevention Tips]
1. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and moderate exercise.
2. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as alcohol is a common cause of liver damage.
3. Have regular physical examinations, especially for people with a family history of liver disease.
4. Pay attention to personal hygiene and avoid contact with environments that may transmit hepatitis viruses.