Secozil, also known as difenoconazole or oxadiazine, belongs to the triazole class of fungicides . It is popular due to its high efficiency, broad spectrum, low toxicity, and low dosage. So, what diseases does Secozil fungicide treat? Let's find out below.
What diseases does Shigao fungicide treat?
Shigao fungicide is effective against many diseases and can control black spot, black rot, white rot, leaf spot, powdery mildew, brown spot, rust, stripe rust, Fusarium head blight, etc.

Features of Shigao bactericide
1. Good systemic absorption
Shigao fungicide is systemic and has a broad spectrum of fungicides. It can be absorbed by plants and has strong penetration. It is absorbed by crops within 2 hours after application and has the characteristic of upward conduction, which can protect newly emerging leaves, flowers and fruits from pathogens.
2. Long-lasting effect
Shigao fungicide is rain resistant and has a long-lasting effect. The fungicide adhering to the leaf surface is resistant to rain washout and has very little volatilization from the leaves. Even under high temperature conditions, it exhibits long-lasting fungicidal activity, with an effective period of 3 to 4 days longer than that of ordinary fungicides.
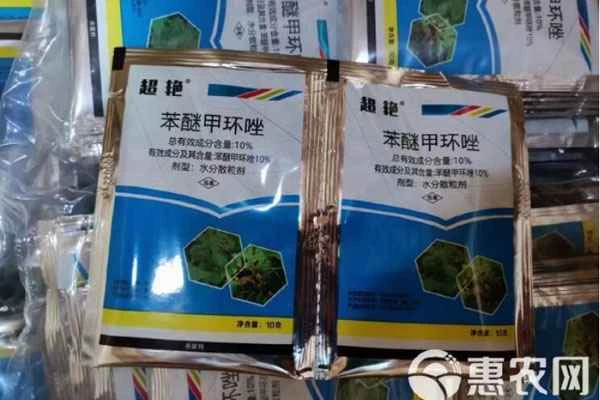

3. Good compatibility
Shiga fungicide can be mixed with a variety of insecticides and fungicides such as imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, propiconazole, azoxystrobin, tebuconazole, prochloraz, and thiophanate-methyl to further broaden the fungicidal spectrum and improve the control effect.
4. Good security
Shiga fungicide is currently the safest triazole fungicide available. It can be used for spraying or seed treatment, controlling diseases while promoting root growth and increasing yield. It rapidly disintegrates and disperses in water, forming a highly suspended dispersion system with no dust impact, making it safe for users and the environment. It contains no organic solvents and is safe for recommended crops.
5. Broad-spectrum bactericidal activity
Shiga fungicide has a long-lasting protective and curative effect on Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes, and Deuteromycetes including Alternaria, Diplosporium, Cercospora, Colletotrichum, Coccidioidomyces, Stem-tipterus, Cynosporium, Syncosporium, and Nelumbo, as well as Powdery mildew family, Rustales order and certain species-borne pathogens.