Seborrheic dermatitis is a common type of chronic dermatitis.
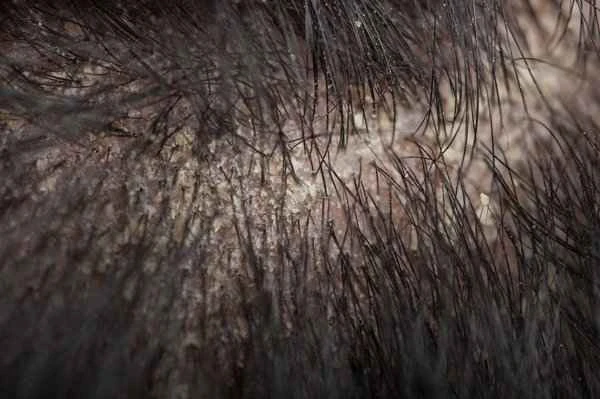
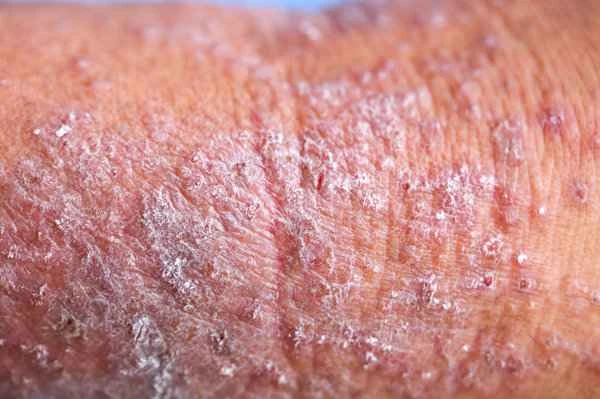
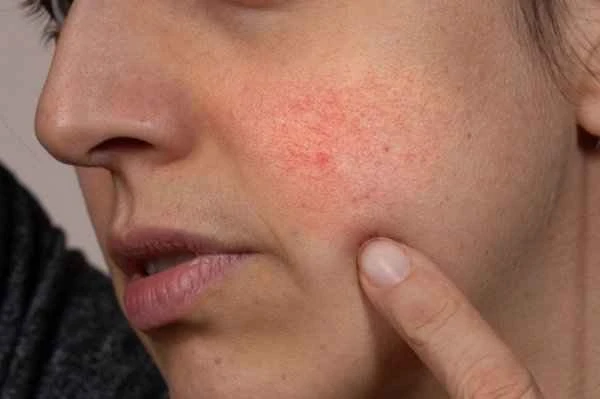
Seborrheic dermatitis is important because it affects the quality of life for many people, and understanding its nature helps in timely management and treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis mainly occurs in areas with a high concentration of sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest, and is characterized by erythema, scaling, and an oily feel. This type of dermatitis is related to excessive sebum secretion, Malassezia overgrowth, and genetic factors. Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis typically involves the use of antifungal medications, corticosteroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Maintaining good personal hygiene is also an important part of treatment. It is important to note that the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is a long-term process, requiring patients to be patient, follow their doctor's instructions, and have regular follow-up appointments to monitor changes in their condition. During treatment, patients should avoid stopping medication or changing their treatment plan on their own to prevent recurrence or worsening of the condition.
【Useful Tips:】
1. Maintain good personal hygiene habits and clean the affected skin area regularly.
2. Use medications recommended by your doctor, such as antifungal creams or lotions.
3. Avoid using cosmetics or skincare products that may irritate the skin.
4. Have regular follow-up visits and follow the doctor's instructions for long-term management.


