Many people are unsure how many peanut seeds to plant. Generally, it's best not to plant too many seeds, as overcrowding will hinder growth. Maintaining adequate spacing is sufficient. So, how many seeds should you plant? Let's find out.
How many seeds should you plant when planting peanuts?
When planting peanuts, it is common practice to use two to four seeds, and the spacing between plants and rows should be carefully controlled. However, the specific number of seeds should also take into account factors such as soil fertility and variety.
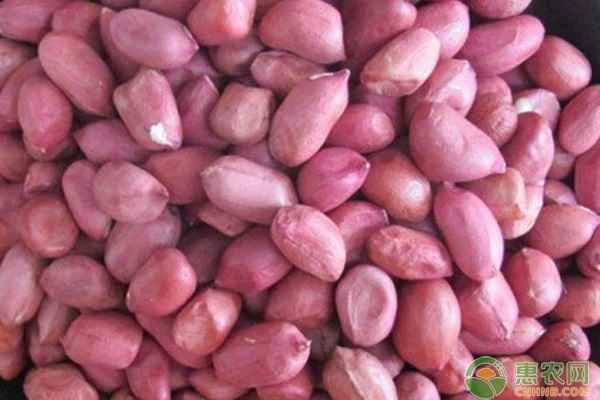

What are the different types of peanut seeds ?
1. Standard type
Common peanut seeds are oval-shaped, with a seed coat that is mostly light red to red, and a few varieties are brown or dark red. Germination requires a relatively high temperature, with a lower limit of 15℃, and the seeds have a long dormancy period, generally more than 50 days.
2. Pearl -shaped
Pearl-type peanut seeds are round or peach-shaped. The seed coat is smooth, generally light red, thin, and glossy. They have a short growing season, 120-130 days for spring sowing, and a very short dormancy period, easily germinating naturally in the field upon maturity.
3. Multi-particle type
Multi-kernel peanut seeds are mostly irregular in shape, slightly conical, cylindrical, or triangular. They have a short dormancy period, germinate quickly, and produce strong, concentrated seedlings. They are suitable for planting in areas with short frost-free periods and low temperatures.
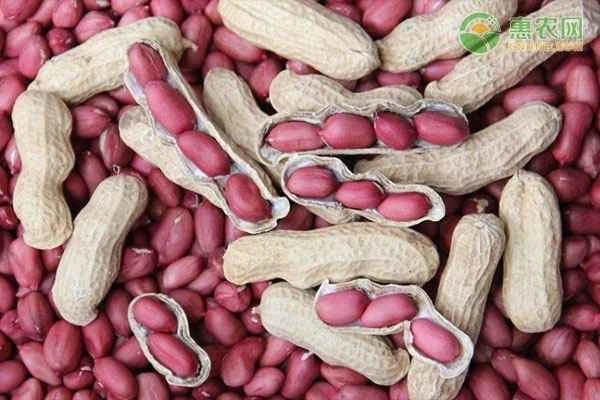

4. Dragon-shaped
Longsheng-type peanut seeds have a longer dormancy period, and germination and seedling growth are slower. However, their seeds have a high protein content, giving them a unique aroma when processed for consumption . The general growth period is about 150 days.
5. Intermediate type
Intermediate-type peanut seeds are oval or flattened oval, with strong germination ability and moderate dormancy. A small number of seeds may germinate at harvest. This type of variety is characterized by high and stable yields, and its adoption has been rapid since the 1980s, showing great potential for development in peanut-producing areas.