Celery has good adaptability, prefers warm and cool temperatures but is not tolerant of heat, and is also relatively cold-resistant. It has high nutritional value, and winter celery is tender and delicious. When planting overwintering celery, it is important to select varieties with excellent quality, tolerance to low light, cold resistance and disease resistance. Below, we will discuss the field management techniques for celery in January.
1. Seedling management
Celery is quite cold-resistant and prefers cool conditions. To ensure uniform germination, provide a suitable environment. First, avoid direct sunlight by erecting shade netting over the seedbed. Water the soil before sowing to increase soil moisture and lower the temperature, while also keeping the soil loose to prevent seedlings from suffocating due to lack of oxygen. After the seedlings emerge, maintain a temperature of 10-20 degrees Celsius. When they have 3-4 true leaves, maintain a spacing of about 2 cm between seedlings and thin them out promptly.
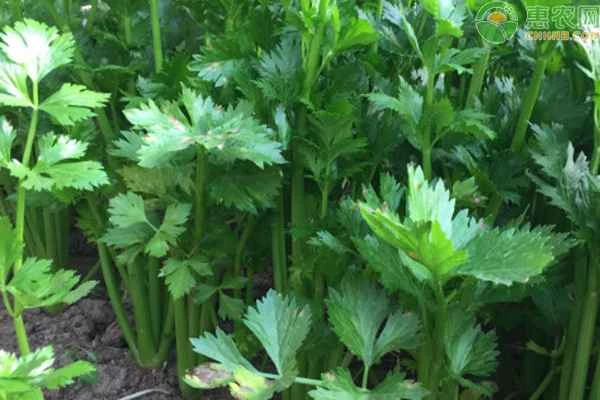

2. Planting Management
When the seedlings have grown to 5-6 true leaves, they can be transplanted. Before transplanting, prepare the land and fertilize it. Depending on the soil fertility, apply an appropriate amount of organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer per acre, and mix the soil and fertilizer evenly before making ridges. Water thoroughly when transplanting the seedlings, and transplant them with soil attached. Pay attention to grading and transplanting, and do not damage the root system. Plant at a reasonable density, ensuring that the original soil depth of the seedlings is the same as the soil depth at transplanting, leaving the central leaves exposed. Water promptly after transplanting to help the seedlings recover.

3. Cold protection and heat preservation
Celery thrives in temperatures between 15-20 degrees Celsius, with a maximum temperature not exceeding 22 degrees Celsius. When temperatures are high, ventilation and watering should be increased to control the temperature. When temperatures drop, ventilation should be reduced, and a thin film should be used to cover the plant to maintain a suitable temperature, which should not fall below 10 degrees Celsius. The amount of sunlight also affects its growth. Celery is a low-light plant, but controlling sunlight in winter can easily cause it to bolt prematurely, affecting quality and yield. Generally, 6-9 hours of sunlight per day is optimal.
4. Fertilizer and water management
After transplanting, strengthen fertilizer and water management, and promptly spray "New High-Lipid Film" for disinfection, disease prevention, moisture retention, and waterlogging prevention. Prevent sun exposure and water loss to effectively reduce the occurrence of various pests and diseases and ensure normal growth and development. Under the premise of strengthened management, spraying the growth regulator "Vegetable and Fruit Strengthening Agent" can inhibit vegetative growth, promote reproductive growth, and prevent celery from bolting and flowering.

5. Harvest at the right time
Harvesting by plucking leaves or harvesting before the flower stalks emerge can reduce the damage caused by premature bolting.