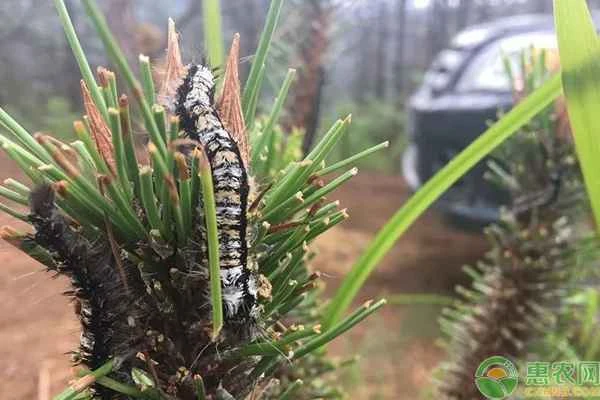
The larch caterpillar is a major pest of pine forests. Its main characteristic is that it eats the needles, and in large outbreaks, it can deplete the needles, causing entire pine trees to die. So how can we control the larch caterpillar? Let's learn about the methods below.
1. Forest management and control
Establish mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests, transform artificial monoculture forests into mixed forests, do a good job of closing mountains for afforestation, prevent heavy pruning, and improve the self-control ability of trees; pay attention to pruning branches with insects, manually remove cocoons during the pupal stage of pests (late June), and manually capture caterpillars during the peak larval stage, taking care to avoid poisonous hairs when capturing them.

2. Trunk mulch
First, remove the old bark and scraped bark from the trunk of the larch tree to make it smooth. Then, wrap the larch trunk with plastic film 2-3 times. After wrapping, staple the film securely. Finally, cut off any excess plastic film. This method of control is cheaper and more effective than chemical control .
3. Physical prevention and control
During the peak emergence period of adult insects, black light lamps or frequency-vibration insecticidal lamps can be used to lure and kill the adults.
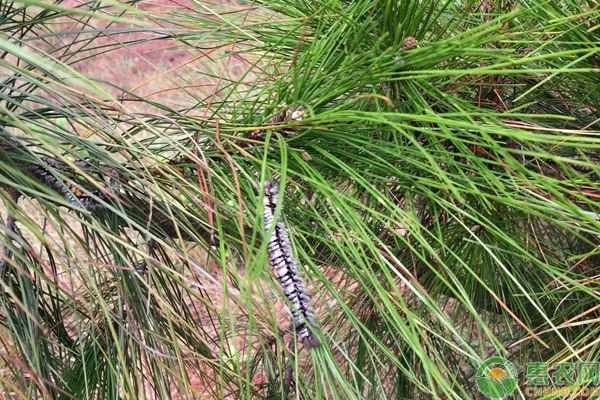

4. Biological control
Artificial bird boxes can be hung to attract beneficial birds, such as great tits, owls, and magpies. Alternatively, in early to mid-July each year, during the peak egg-laying period of adult insects, Trichogramma wasps can be released to control the insects.
5. Chemical control
Control should ideally be implemented during the early larval stages. At this time, the insect population density is low, the damage is minimal, and the insects' resistance to pesticides is relatively weak. For control, spray with a 1000-fold dilution of 45% propiconazole, a mixture of a 1500-fold dilution of 20% cypermethrin and a 2000-fold dilution of 5.7% abamectin, or a 1500-2000-fold dilution of 40% acetamiprid (Bizhi). 1-2 applications can be given, with an interval of 7-10 days. Rotate pesticides to delay the development of resistance.
In addition, for pine caterpillars that come down from the tree to overwinter, poison pens, poison paper, poison ropes made of pyrethroid insecticides can be applied to the tree trunks before they come up to the tree in spring and before they come down in autumn to kill the larvae that come down to overwinter and those that come up to the tree.